thickness of stratospheric ozone layer is measured in|Dobson Units : importing View all of the Antarctic Hemisphere daily maps of total ozone for October 2024. . Nossa clínica de massagem em Santana foi planejada estrategicamente para oferecer um ambiente sereno e relaxante. Com salas exclusivas e meticulosamente decoradas, .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webFree gay porn videos, huge collection of free gay porno movies. New gay men twink sex porn tube vids delivered to you everyday only at BoyFriendTV.com
The Dobson Unit is a way to describe how much ozone there would be in the column if it were all squeezed into a single layer. The average amount of ozone in the atmosphere is roughly 300 Dobson Units, equivalent to a layer 3 millimeters (0.12 inches) .Ozone hole facts. These reactions convert the inactive chlorine reservoir chemicals .View all of the Antarctic Hemisphere daily maps of total ozone for October 2024. .Ground-based Dobson spectrometers are still in use, around the world, to .
Q. Ozone layer thickness is measured in units. Q. UV rays act on chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and release __________ which degrades the ozone layer in the stratosphere.Ozone measurements. Ozone is meas-ured throughout the atmosphere with instruments on the ground and on board aircraft, high-altitude balloons, and satellites. Some instruments measure .
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in relation to other gases in the stratosphere. The ozone layer contains less than 10 parts per million of ozone, while the average ozone concentration in Earth's atmospher.Atmospheric Ozone is one of the most important trace gases in our atmosphere that both benefits and harms life on Earth. High ground-level ozone amounts contribute to poor air quality, .
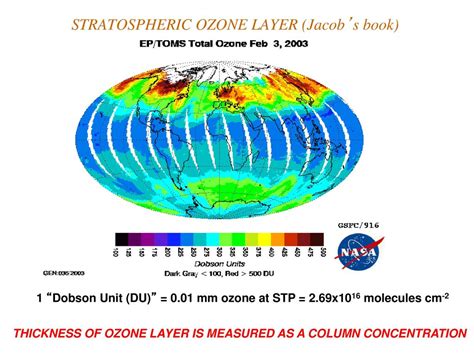
The ozone layer's thickness is not solely controlled by chemical processes in the stratosphere. As an atmospheric trace gas, O 3 is also transported over large distances by stratospheric winds, which significantly affects global ozone .As a result of human emissions of ozone-depleting substances, concentrations of ozone in the stratosphere – between 10 to 50 kilometers above the earth's surface – fell rapidly throughout the 1970s, ‘80s, and early ‘90s. This is shown .Ground-based Dobson spectrometers are still in use, around the world, to document the abundance of stratospheric ozone. A Dobson unit represents the thickness of an atmospheric .
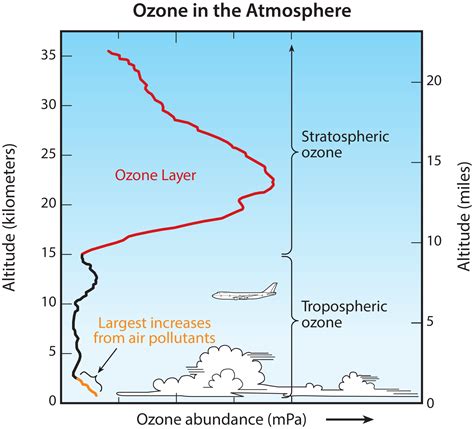
The Dobson Unit. The Dobson Unit (DU) is a unit of measurement of ozone found in a column of air stretching from the surface of Earth to the edge of the atmosphere. It is given as the thickness of the layer formed by ozone .Most ozone (about 90%) resides in a layer that begins between 6 and 10 miles (10 and 17 kilometers) above the Earth's surface and extends up to about 30 miles (50 kilometers). This region of the atmosphere is called the stratosphere.The stratospheric ozone layer extends over the entire globe, with some variation in its altitude and thickness. Most of the remaining ozone (about 10%) is found in the troposphere, which is the lowest region of the atmosphere, .
The ozone layer ozone layerThe region of the stratosphere containing the bulk of atmospheric ozone. The ozone layer lies approximately 15-40 kilometers (10-25 miles) above the Earth's surface, in the stratosphere. . Scientists use balloons, aircraft, and satellites to measure the composition of the stratosphere. These measurements show a .The correct option is B Dobson units. The ozone layer was discovered in 1913 by the French physicists Charles Fabry and Henri Buisson. Its properties were explored in detail by the British meteorologist G. M. B. Dobson, who developed a simple spectrophotometer (the Dobson Miter) that could be used to measure stratospheric ozone from the ground.
Explanation-. The ozone layer is present in the stratosphere at a height of 16km to 25km.; Ozone thickness is measured by Dobson units(D.U.); Ozonosphere works as a shield against UV radiation.; Depletion in the concentration of the ozone layer called the ozone hole was first discovered by the Nimbus-7 satellite (1985).; The aerosols like C.F.C (chloro fluoro carbon) .
Stratospheric ozone (sometimes referred to as "good ozone") plays a beneficial role by absorbing most of the biologically damaging ultraviolet sunlight (called UV-B), allowing only a small amount to reach the Earth's surface. . Ground-based and satellite instruments have measured decreases in the amount of stratospheric ozone in our . Ninety percent of the ozone in the atmosphere sits in the stratosphere, the layer of atmosphere between about 10 and 50 kilometers altitude. The natural level of ozone in the stratosphere is a result of a balance between sunlight that .Stratosphere. The next layer up is called the stratosphere. The stratosphere extends from the top of the troposphere to about 50 km (31 miles) above the ground. The infamous ozone layer is found within the stratosphere. Ozone molecules in this layer absorb high-energy ultraviolet (UV) light from the Sun, converting the UV energy into heat.
The thickness of stratospheric ozone layer is measured in/on.
Reduced ozone levels as a result of ozone depletion ozone depletionA chemical destruction of the stratospheric ozone layer beyond natural reactions. Stratospheric ozone is constantly being created and destroyed through natural cycles. . (nm) is a common measure of the wavelength of light; 1 nm equals one billionth of a meter (=10–9 m .
weight, ozone-measuring modules suitable for launching on small balloons. The balloons ascend far enough in the atmosphere to measure ozone in the stratospheric ozone layer. Ozonesondes are launched regularly at many loca-tions around the world. Local ozone-measuring instru - ments using optical or chemical detection schemes areand forming a layer of pure ozone that extends over the entire globe. The resulting layer would have an average thickness of about three millimeters (0.12 inches) (see Q3). Nonetheless, this extremely small fraction of the atmosphere plays a vital role in protecting life on Earth (see Q2). Stratospheric ozone.Stratospheric ozone is formed naturally NASA began measuring Earth’s stratospheric ozone layer by satellite in 1979. By the time the Montreal Protocol went into effect in 1989, ozone concentrations (in Dobson units) had declined significantly over the Antarctic, enlarging the ozone hole. . Ozone was also measured by instruments on satellites orbiting Earth, though satellite .
The stratosphere is Earth's second lowest atmospheric layer. It contains approximately 90 percent of all atmospheric ozone. The researchers concluded the Earth's protective ozone layer outside of the polar regions stopped thinning around 1997. Ozone in these areas declined steadily from 1979 to 1997.
The ozone hole is a loss of stratospheric ozone over Antarctica.The ozone hole area is defined as the size of the region with total ozone below 220 Dobson units (DU). Dobson Units are a unit of measurement that refer to the thickness of the ozone layer in a vertical column from the surface to the top of the atmosphere, a quantity called the "total column ozone amount."The stratosphere is a layer of Earth's atmosphere. It is the second layer of the atmosphere as you go upward. The troposphere, the lowest layer, is right below the stratosphere. . They appear to help cause the formation of the infamous holes in the ozone layer by "encouraging" certain chemical reactions that destroy ozone.the atmosphere to measure ozone in the stratospheric ozone layer. Ozonesondes are launched weekly at many locations around the world. Direct ozone-measuring instruments using optical or chemical detection schemes are also used routinely on board research aircraft to measure the distribution of ozone in the troposphere and lower stratosphere.The stratospheric ozone layer extends over the entire globe, with some variation in its altitude and thickness. Most of the remaining ozone (about 10%) is found in the troposphere, which is the lowest region of the atmosphere, .
The thickness of the ozone layer in a column of air is measured in Dobson units (DU). One DU represents the amount of ozone molecules needed to produce a 0.01-millimetre layer of pure ozone at Earth’s surface. . At NOAA’s South Pole Baseline Atmospheric Observatory, scientists measure the layer’s thickness by releasing weather balloons carrying ozonesondes and by making ground-based measurements with a Dobson spectrophotometer. . “This year, we observed about 95% depletion where we often see near 100% loss of ozone within the stratosphere.” .
ber of ozone molecules needed to make a layer of ozone 0.01 mm thick. However, in practical use, the Dobson unit is based on the thickness a layer of ozone would be if all the ozone in a column between the Earth’s surface and space were held at standard tem-perature and air pressure (1013.25 millibars or 1 atmosphere). That layer would be 0.3 .
ozone-measuring modules suitable for launching on small bal-loons. The balloons ascend up to altitudes of about 32 to 35 kilo - meters (km), high enough to measure ozone in the stratospheric ozone layer. Ozonesondes are launched regularly at many loca-tions around the world. Local ozone-measuring instruments ozone layer, region of the upper atmosphere, between roughly 15 and 35 km (9 and 22 miles) above Earth’s surface, containing relatively high concentrations of ozone molecules (O 3).Approximately 90 percent of the atmosphere’s ozone occurs in the stratosphere, the region extending from 10–18 km (6–11 miles) to approximately 50 km (about 30 miles) above Earth’s .
Strato and Troposhperic Ozone
Section I: Ozone in our atmosphere 11 How is ozone measured in the Q4 atmosphere? The amount of ozone in the atmosphere is measured by instruments on the ground and carried aloft on balloons, aircraft, and satellites. Some instruments measure ozone remotely over long distances by using ozone’s unique optical absorption or emission properties.
The hole in the ozone layer — the portion of the stratosphere that protects our planet from the sun’s ultraviolet rays — is continuing to decrease. The hole over Antarctica had an average area of 8.91 million square miles (23.2 million square kilometers). That measurement is slightly smaller than the extent of 8.99 million squareExplanation-. The ozone layer is present in the stratosphere at a height of 16km to 25km.; Ozone thickness is measured by Dobson units(D.U.); Ozonosphere works as a shield against UV radiation.; Depletion in the concentration of the ozone layer called the ozone hole was first discovered by the Nimbus-7 satellite (1985).; The aerosols like C.F.C (chloro fluoro carbon) . forcing and health. For example, stratospheric ozone (~10-50km) is typically seen as “good” ozone, whereas tropospheric ozone (~7-20km), or ozone near the boundary layer where humans live and breathe, is typically seen as “bad” ozone. • Stratospheric ozone, climate and health: Naturally occurring stratospheric ozone acts as a protective
Ground-level ozone (O 3) forms when volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react with nitrogen oxide emissions in the presence of sunlight. Ozone is harmful to humans when they breathe it in and to plants when they respire. Monitoring ozone concentrations in parks helps us to determine air quality trends, provide public health alerts, and assess compliance with .Ozone is spread from the surface of Earth upto the top of stratosphere, 50 km as a very thin layer. The question often asked is how is the concentration of ozone in this thin layer is measured and quantified with a reasonable accuracy. Atmospheric ozone is measured both by remote sensing and by in-situ techniques.

Miracle Mile Shops. Planet Hollywood Resort and Casino. Las Vegas Strip, Central. 0.26 miles (0.41 km) from Bellagio Fountains. Located at the heart of the Las Vegas Strip, .
thickness of stratospheric ozone layer is measured in|Dobson Units